Crohn’s Disease – All you need to Know about

Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that affects millions of people worldwide. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Crohn’s disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies.
Whether you’re newly diagnosed or seeking to deepen your understanding, this article aims to provide valuable insights into this complex condition.
Understanding Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease primarily targets the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, causing inflammation that can extend deep into the layers of the affected bowel tissue.
While the exact cause of Crohn’s remains unknown, a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors is believed to contribute to its development.
Genetic Factors
Research indicates a genetic predisposition to Crohn’s disease, with certain gene mutations increasing the risk of its occurrence. Individuals with a family history of IBD may have a higher likelihood of developing Crohn’s.
Environmental Factors – Crohn’s Disease
Environmental factors also play a role in the development of Crohn’s disease. Factors such as diet, smoking, and exposure to certain infections have been linked to an increased risk of developing the condition. Researchers continue to investigate the specific environmental triggers associated with Crohn’s.
Immune System Dysfunction
An abnormal immune response is a key element in the development of Crohn’s disease. In individuals with Crohn’s, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the GI tract, leading to chronic inflammation.
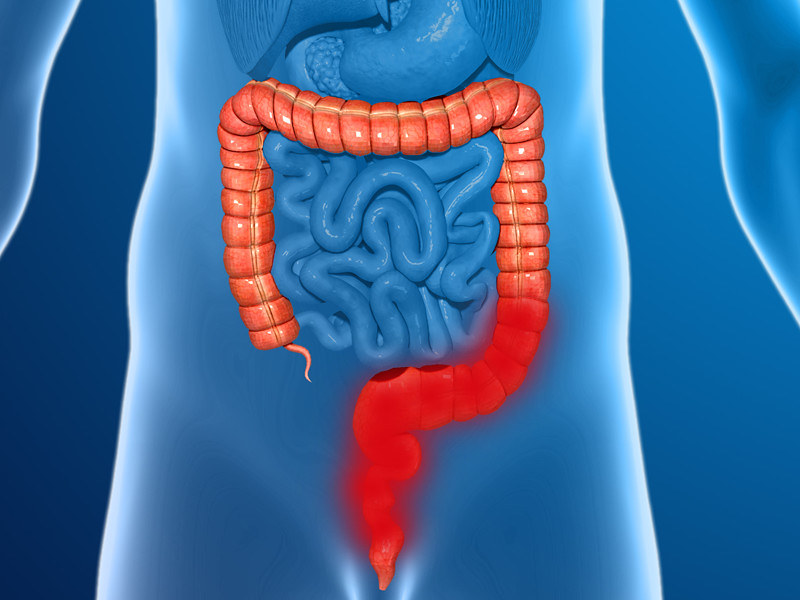
Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
The disease can manifest with a variety of symptoms that range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Reduced appetite
- Fever
- Rectal bleeding
It’s important to note that symptoms can vary widely among individuals, and some may experience periods of remission with little to no symptoms.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Diagnosing Crohn’s conditon involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. These tests may include blood tests, imaging studies (such as CT scans and MRIs), endoscopy, and biopsy. A definitive diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Treatment Approaches
While there is currently no cure for Crohn’s disease, various treatment options aim to manage symptoms, induce remission, and prevent flare-ups. Treatment plans are often personalized based on the severity of the condition and individual patient factors. Common treatment approaches include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and biologics are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and modulate the immune response.
- Nutritional Therapy: Some individuals benefit from dietary changes, including the use of specialized nutritional formulas.
- Surgery: In cases of severe complications, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged portions of the GI tract.
Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations
Managing Crohn’s disease extends beyond medical interventions. Lifestyle and dietary modifications can significantly impact symptom control and overall well-being. Consider the following tips:
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Focus on a well-balanced diet rich in nutrients, and consider working with a dietitian to identify trigger foods.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is essential, especially during periods of active symptoms.
- Monitor Stress: Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises, can help mitigate the impact of stress on symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can contribute to overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Crohn’s disease is a challenging condition that requires a multidimensional approach to management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals with Crohn’s and their caregivers can navigate the complexities of this chronic condition more effectively.
Ongoing research continues to shed light on new therapeutic avenues, offering hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for those affected by the disease.
Related Articles
About the Author




0 Comments