Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that significantly affects the digestive system. It is a complex condition with a multitude of symptoms, causes, and treatment options. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Crohn’s disease, drawing from reputable sources such as Mayo Clinic, NHS, and Cleveland Clinic.
What is Crohn’s Disease?
Crohn’s disease is a type of IBD that causes inflammation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Unlike other IBDs, Crohn’s can affect any part of the GI tract, from the mouth to the anus, although it most commonly targets the end of the small intestine (ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (colon). The inflammation often spreads deep into the layers of affected bowel tissue, which can be painful and debilitating, and sometimes leads to life-threatening complications.
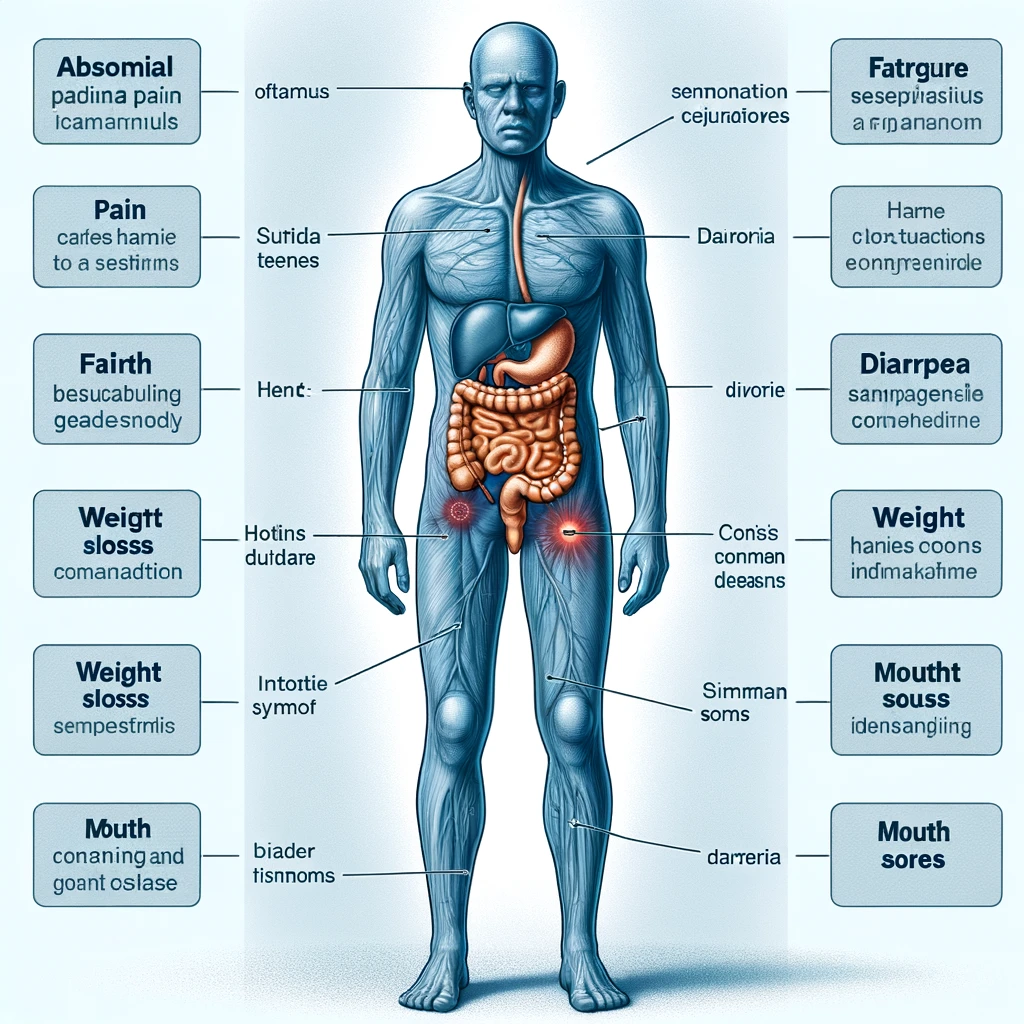
Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease can vary significantly from person to person and may develop gradually or come on suddenly. They include:
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Blood in stool
- Mouth sores
- Reduced appetite and weight loss
- Inflammation of skin, eyes, and joints
- Anemia (due to blood loss)
Children with Crohn’s disease may suffer from delayed growth and development. It’s important to note that symptoms can flare up and then be followed by periods of remission
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of the disease is unknown, but it’s believed to result from an abnormal immune response that causes the immune system to attack the digestive tract. This may be triggered by genetic and environmental factors, including:
- Family history: A higher risk if a close family member has the condition.
- Age: Most people are diagnosed before 30.
- Ethnicity: Higher risk in whites, particularly of Ashkenazi Jewish descent.
- Smoking: Increases risk and severity.
- NSAIDs: Can aggravate symptoms.
- Diet and lifestyle: High-fat diets and urban living may increase risk.
Diagnosing Crohn’s Disease
Diagnosing Crohn’s disease can be challenging due to its similarities with other GI disorders. A combination of tests is used:
- Blood tests to check for anemia and infection.
- Stool studies to rule out other causes of symptoms.
- Colonoscopy to examine the entire colon and end of the ileum.
- Imaging tests like CT scans and MRI for detailed views of the GI tract.
- Capsule endoscopy and balloon-assisted enteroscopy for further investigation.
Treatment Options
There’s currently no cure for it, but treatments can greatly reduce its signs and symptoms and even bring about long-term remission:
- Medications: These include anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system suppressors, antibiotics, and biologics.
- Nutritional Therapy: Special diets and supplements can help manage symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery to remove damaged sections of the digestive tract may be necessary.
Treatment plans often involve a combination of approaches and depend on the severity and location of the diseas.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alongside medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms:
- Diet changes: Avoiding foods that trigger symptoms.
- Regular exercise.
- Stress management techniques.
- Avoidance of NSAIDs and smoking cessation.
Complications of Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease can lead to numerous complications, including:
- Bowel obstruction
- Ulcers
- Fistulas
- Anal fissures
- Malnutrition
- Colon cancer
- Other health issues such as liver disease, osteoporosis, and skin condition.
Living with Crohn’s Disease
Living with Crohn’s disease can be challenging, but many people with the condition lead active, fulfilling lives. It’s important for those with Crohn’s to:
- Understand their condition and treatment options.
- Maintain regular checkups and adhere to treatment plans.
- Seek support from healthcare professionals and support groups.
Conclusion
Crohn’s disease is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach for management. Understanding the disease, its symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for those affected and their loved ones. With advances in medical science, people with Crohn’s can hope for better management of their symptoms and an improved quality of life. Regular consultation with healthcare providers and adherence to treatment plans are essential for managing this chronic condition.
Related Articles
About the Author




0 Comments